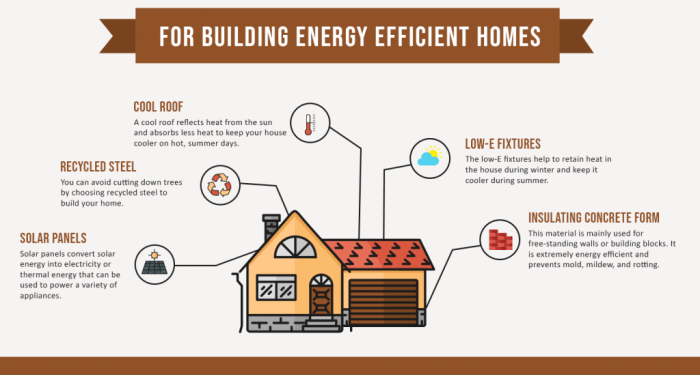
Exploring the realm of energy-efficient exterior materials for buildings, this topic delves into the importance of sustainable construction practices and the key characteristics that define energy efficiency. From commonly used materials to innovative technologies, this discussion aims to shed light on how choices in building materials can impact the environment and energy consumption.
As we navigate through the different types of energy-efficient exterior materials and considerations for selection, we uncover a world where smart technologies and renewable energy sources merge to create a more sustainable future for building exteriors.
Energy-efficient exterior materials for buildings
Energy-efficient exterior materials play a crucial role in sustainable construction by reducing energy consumption, lowering utility costs, and minimizing environmental impact. These materials help regulate indoor temperatures, enhance insulation, and improve overall energy efficiency of buildings.
Examples of commonly used energy-efficient exterior materials:
- Insulated Concrete Forms (ICFs): These materials provide superior insulation properties, reduce air infiltration, and offer high thermal mass.
- Double-glazed windows: Double-pane windows with low-emissivity coatings help minimize heat loss and gain, improving energy efficiency.
- Green roofs: Vegetated roof systems offer natural insulation, reduce urban heat island effect, and promote biodiversity.
Key characteristics that make exterior materials energy-efficient:
- High thermal resistance: Materials with high R-values help prevent heat transfer through walls, roofs, and windows.
- Air tightness: Exterior materials that reduce air leakage contribute to better insulation and energy conservation.
- Solar reflectance: Surfaces with high solar reflectance index (SRI) reflect sunlight and reduce heat absorption, lowering cooling loads.
Types of energy-efficient exterior materials
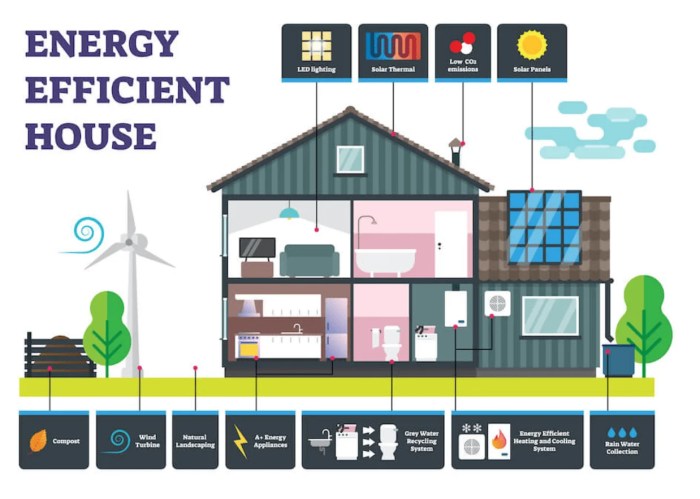
When it comes to energy-efficient exterior materials for buildings, there are several options available that can help improve sustainability and reduce energy consumption. Let's explore some of the common types of energy-efficient exterior materials used in construction.
Comparison of Energy-Efficient Exterior Materials
| Material Type | Description | Energy Efficiency Rating | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insulated Concrete | Insulated concrete combines concrete with insulation materials to create a strong and energy-efficient building material. | High | Medium-High |
| Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs) | SIPs consist of a foam core sandwiched between two structural facings, providing excellent insulation and structural support. | High | Medium |
| Green Roofs | Green roofs are covered with vegetation, providing natural insulation, reducing heat absorption, and promoting biodiversity. | Medium-High | High |
Environmental Impact of Energy-Efficient Exterior Materials
Using energy-efficient exterior materials in construction can have a positive impact on the environment. These materials help reduce energy consumption, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and promote sustainability by improving the overall efficiency of buildings. Additionally, materials like green roofs can help mitigate urban heat island effects and improve air quality in urban areas.
Innovative technologies in energy-efficient exterior materials
Advancements in technology have revolutionized the development of energy-efficient materials for building exteriors, offering sustainable solutions to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact.
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
The integration of renewable energy sources such as solar panels and green facades has significantly contributed to enhancing the energy efficiency of building exteriors. Solar panels harness sunlight to generate electricity, reducing reliance on traditional power sources and lowering carbon emissions.
Green facades, made up of living plants, provide natural insulation, improve air quality, and reduce the urban heat island effect.
Smart Technologies for Energy Efficiency
Smart technologies play a crucial role in optimizing the energy efficiency of building exteriors. From automated shading systems that adjust according to sunlight intensity to sensors that regulate heating and cooling based on occupancy levels, these technologies help minimize energy wastage and ensure optimal building performance.
Additionally, smart facades with dynamic thermal properties can adapt to external conditions, reducing the need for mechanical heating and cooling.
Considerations for selecting energy-efficient exterior materials
When choosing energy-efficient exterior materials for buildings, there are several important factors to consider to ensure maximum benefits and improved energy performance.
Role of Insulation, Thermal Mass, and Air Sealing
Insulation, thermal mass, and air sealing play crucial roles in enhancing the energy efficiency of building exteriors. Insulation helps in reducing heat transfer through the building envelope, keeping the interior temperature stable and reducing the need for heating or cooling.
Thermal mass absorbs and stores heat, regulating indoor temperatures and reducing energy consumption. Air sealing prevents air leakage, improving the overall efficiency of the building envelope.
- Choose insulation materials with high R-values to effectively reduce heat transfer.
- Opt for materials with high thermal mass, such as concrete or stone, to stabilize indoor temperatures.
- Ensure proper air sealing around windows, doors, and other openings to prevent energy loss.
Tips for Optimizing Energy-Efficient Materials
To maximize the benefits of energy-efficient exterior materials, consider the following tips:
- Conduct a thorough energy audit to identify areas of improvement and prioritize upgrades.
- Select materials that are locally sourced to reduce environmental impact and transportation costs.
- Combine different energy-efficient materials strategically to create a balanced and effective building envelope.
- Regularly maintain and inspect the exterior materials to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Concluding Remarks
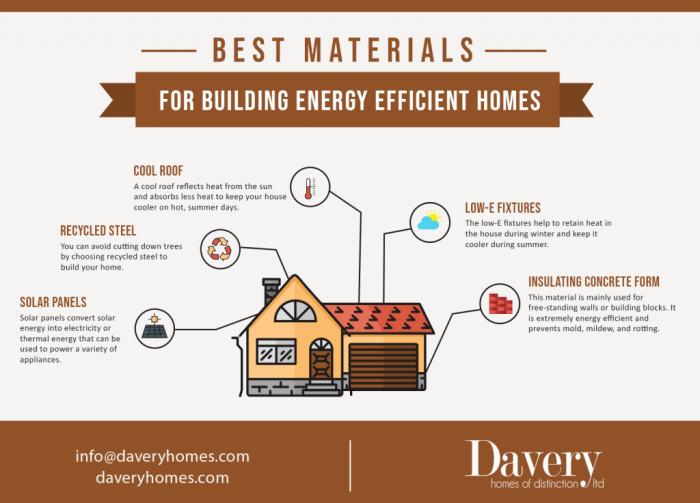
In conclusion, the journey through energy-efficient exterior materials for buildings highlights the significance of making informed choices that not only benefit the environment but also contribute to long-term energy savings. By understanding the impact of materials on energy efficiency, we pave the way for more sustainable and eco-friendly construction practices in the future.
FAQ Insights
What are some examples of commonly used energy-efficient exterior materials?
Common examples include insulated concrete, structural insulated panels, and green roofs.
How do smart technologies enhance the energy efficiency of building exteriors?
Smart technologies can optimize energy consumption by regulating heating, cooling, and lighting systems based on real-time data and user preferences.
What role does insulation play in improving the energy performance of building exteriors?
Insulation helps in reducing heat transfer through walls, roofs, and floors, thereby minimizing the need for heating or cooling systems.